Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders, affecting both children and adults. It is characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that can impact various aspects of life, including academic, work, and social settings. While ADHD is often associated with children, it’s important to recognize that it continues into adulthood for many people, presenting unique challenges but also opportunities for growth and understanding.
In this article, we’ll explore the nature of ADHD, common symptoms, its impact on daily life, and how mental health support can help individuals with ADHD thrive.
1. What is ADHD?
ADHD is a brain-based disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate attention and impulses. It is typically diagnosed during childhood, but many adults live with ADHD without having been formally diagnosed. ADHD is divided into three main types, based on the predominant symptoms:
2. Common Symptoms of ADHD
The symptoms of ADHD can vary in intensity and form, but they generally fall into two categories: inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity.
Inattention Symptoms:
Hyperactivity/Impulsivity Symptoms:
These symptoms can make it difficult for individuals with ADHD to stay on top of responsibilities, manage relationships, and perform consistently at school or work.
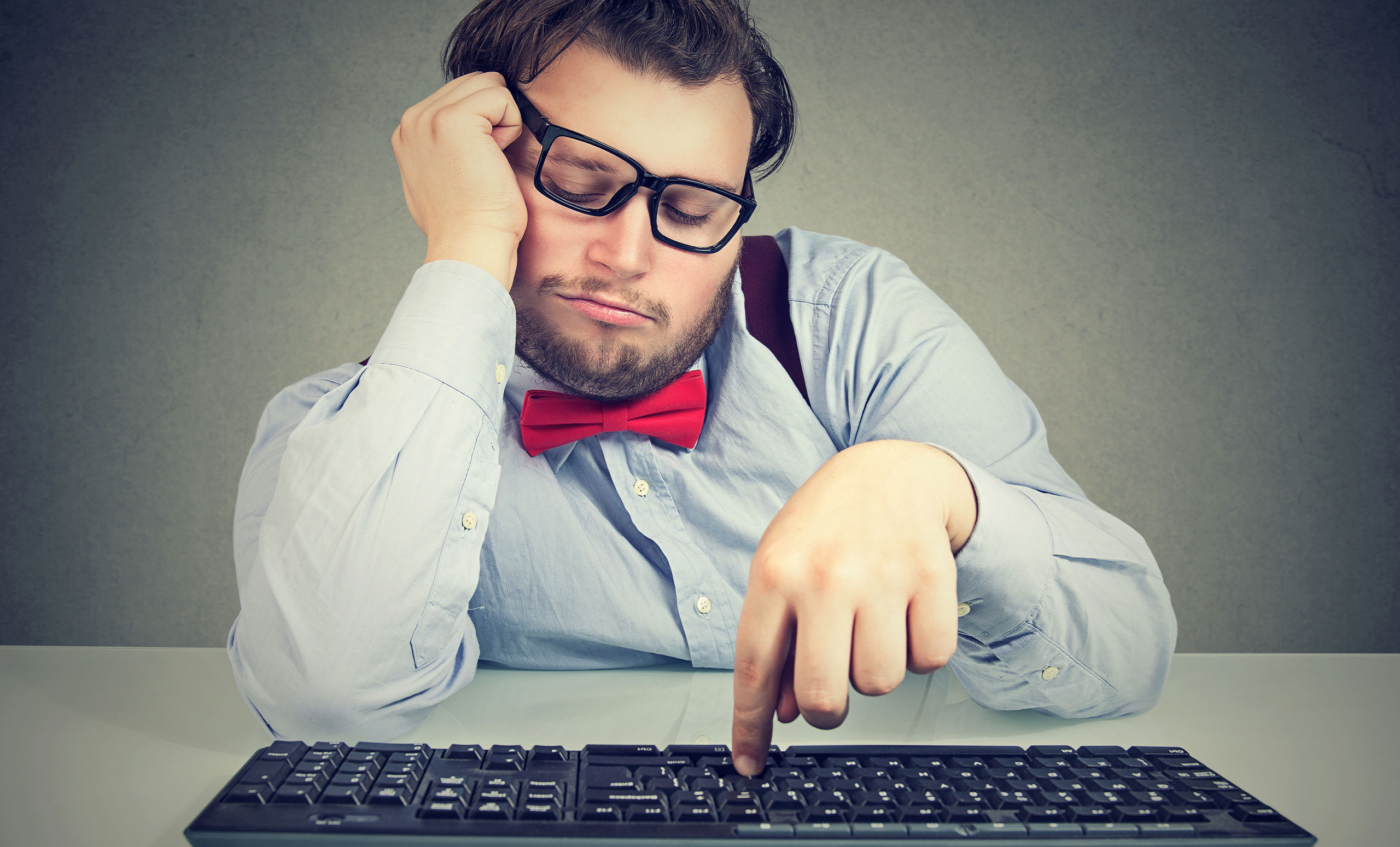

3. ADHD in Adults: What to Look For
While ADHD is often diagnosed in children, many adults go undiagnosed or misdiagnosed for years. In adults, ADHD symptoms can manifest differently than in children. For instance, hyperactivity in children may show up as an inability to sit still, while in adults, it can manifest as internal restlessness or difficulty relaxing.
Common adult ADHD challenges include:
For many adults with undiagnosed ADHD, the disorder can be misunderstood as a lack of motivation, laziness, or carelessness. Recognizing these symptoms and seeking professional support can bring clarity and lead to effective management strategies.
4. The Impact of ADHD on Mental Health
ADHD doesn’t just affect attention and impulse control; it can also have a profound impact on emotional well-being. Living with ADHD can lead to feelings of frustration and low self-esteem, especially if someone has struggled to meet expectations in school, work, or relationships.
Common mental health challenges associated with ADHD include:
Addressing the emotional toll of ADHD through mental health support is key to building a more balanced and fulfilling life.

5. Managing ADHD: A Holistic Approach
While there is no “cure” for ADHD, it is highly manageable with the right strategies and support. The treatment of ADHD often includes a combination of behavioral interventions, counseling, and, in some cases, medication.
Effective ADHD management strategies include:
- 1Behavioral therapy: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly effective for individuals with ADHD. CBT can help individuals reframe negative thought patterns, develop organizational skills, and improve emotional regulation.
- 2Medication: Stimulant medications (such as Adderall and Ritalin) and non-stimulant medications (like Strattera) are commonly prescribed to help manage the core symptoms of ADHD. These medications can improve focus, reduce impulsivity, and help regulate behavior.
- 3Mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Practices like mindfulness meditation can help individuals with ADHD improve focus and emotional regulation by training their attention and helping them remain present in the moment.
- 4Organizational tools: Using planners, reminders, and time management tools can help individuals with ADHD stay organized, meet deadlines, and reduce feelings of overwhelm. Breaking tasks into smaller, more manageable steps can also be useful.
- 5Healthy lifestyle habits: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep are all crucial for managing ADHD symptoms. Physical activity, in particular, can help improve focus and reduce hyperactivity.
- 6Support systems: Engaging with ADHD support groups or seeking therapy can provide a sense of community and shared understanding. Support systems help individuals navigate the challenges of ADHD and reduce feelings of isolation.
6. The Role of Mental Health Professionals in ADHD Support
If you or a loved one suspects ADHD may be affecting your daily life, seeking professional evaluation and support is the first step. A mental health professional, such as a therapist or psychiatrist, can conduct a thorough assessment to determine whether ADHD is present and recommend appropriate treatment.
In therapy, individuals with ADHD can:
At our practice, we specialize in helping individuals with ADHD manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Whether you are seeking a diagnosis, treatment, or ongoing support, we are here to help you on your journey.

Conclusion: Embracing Life with ADHD
ADHD can present significant challenges, but with the right tools and support, individuals with ADHD can thrive. By understanding the disorder, seeking treatment, and developing personalized strategies, it’s possible to navigate life’s demands more effectively and lead a successful, balanced life.
Our mental health practice is here to offer compassionate, evidence-based care to individuals with ADHD at every stage of life.
If you or someone you know is struggling with ADHD, reach out to us today—together, we can find solutions that work for you.